CDNs and GTmetrix
We'll clarify how your GTmetrix score is affected by a Content Delivery Network (CDN) and how your website can work quicker.How does your website do on our CDN recommendation?
The Content Delivery Networks (CDN) overview is a excellent way to make sure your website runs quickly worldwide.
If you are unfamiliar with CDNs, check out why you are using a CDN? Article to know how they're working.
We will discuss in detail in this paper how and why CDNs influence your GTmetrix rating. We will also describe how CDNs function in general and how they assist your tourists globally improve their efficiency.
How are CDNs functioning?
CDNs store the frequently accessed resources of your page worldwide on Edge Servers.
Most CDNs function accordingly; If a customer requests your website, the nearest CDN Edge Server provides the static resource, providing the shortest distance for the information to move; thereby decreasing latency.
This allows users to quickly access the file from their own servers (the source server).
CDNs also help by reducing the stress on your Origin Server by fulfilling requests on its behalf. Most CDNs function accordingly; If a customer requests your website, the nearest CDN Edge Server provides the static resource, providing the shortest distance for the information to move; thereby decreasing latency.
This allows users to quickly access the file from their own servers (the source server).
Instead of your Origin Server handling all the requests from your visitors, the job is now distributed across multiple Edge Servers.
More advanced CDNs can not only cache your static resources, but your entire web application.
For example, Cloudflare caches your entire site (anything pointed to your domain) and hides your Origin Server completely (this is how they protect you from DDoS attacks as well).
General CDN Terminology
Favor to skip this section if you are already experienced with CDNs. However, if you are new to CDNs, you should know some key terms and ideas.
Origin and Edge Servers
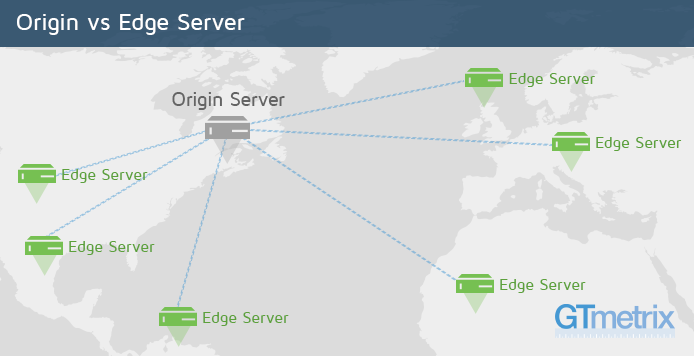
Origin Server is where your entire site is hosted. Edge servers house static resources of your site for faster global delivery.
Origin ServerThe server at which your website is actually hosted. This is wherever your hosting service has its data center. |
Edge ServerOne of the many servers in the CDN’s global network. Your geographic location determines which edge server delivers resources to you. |
Cache Hit
The resource was served from the cache of the Edge Server. The number of cache hits you want, which means that the CDN does not serve your origin server.
This implies that the resource has not been served from the Edge Server cache and that the resource from your original Server is being requested. You want as few cache misses as possible -a high missing cache rate means that the CDN doesn't deliver your funds confidently
Revalidation
This means a request for a resource was made, and the CDN had it cached, but it also performed a check with the Origin Server to see if the cached resource was still valid (i.e. hasn’t changed, still correct to serve, etc.).A failed revalidation is essentially treated as a Cache Miss.
Time to Live (TTL)
Time to deal with an Edge Server cached application. Usually applications pass through revalidation after that moment has elapsed (see above). Typically, CDNs make it possible to adjust TTL to guarantee the recent resources are provided at frequently upgraded locations.
Latency
The length and response time when the application was initiated. The more a visitor is away from a server in a geographical way, the more latency.Routing
Routing is when the customer requests to a specific Edge server are redirected to the CDN. Good routing redirects applications to the customer from the nearest / fastest edge server.
Bandwidth
Bandwidth is capable of referring to the velocity at which the request information is transmitted, or to the quantity of information transmitted through the CDN.
How is the calculation of my CDN score?
YSlow will deduct 10 percent of the "Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)" score for any static submission which is not on a known CDN. The global impact on the complete YSlow score is mild because it is a recommendation of medium priority.
GTmetrix will probably auto-detect this as a suggestion if you are using a famous, common CDN. There is no action required and your rating should reflect the use of CDN. Here are a few popular reasons why you receive an F in this advice:
CDN is not correctly configuredso all services are configured differently. Some of them require a name change, others involve a distinct application to edit URLs of your static demands and others.





